Click here to download Maple worksheet
LIST OF FUNCTIONS
>
with(linalg):
The code consists of two main programs - symm and matrices and two auxiliary functions - simple and l_f.
The program symm is the main function.
The input consists of a complex-valued polynomial f(p) considered as the
projective form of homogeneous binary polynomial F(x,y), and
the degree n=deg(F). The program computes the invariants J and K in reduced form, determines the dimension of the symmetry group, and, in the case of a finite symmetry group, applies the
Maple command solve to solve the two polynomial symmetry equations (3,4) to find
explicit form of symmetries.
The output of symm consists of the projective index of the form and the explicit formulae for its
discrete projective symmetries. The program also notifies the user if the
symmetry group is not discrete, or is in the maximal discrete symmetry class.
| > | symm:=proc(form,n)
global tr,err; local Q,Qp,Qpp,Qppp,Qpppp,H,T,V,U,J,K,j,k, Eq1,Eq2,i,eqtr,ans; tr:='tr': Q:=form(p); Qp:=diff(Q,p); Qpp:=diff(Qp,p); Qppp:=diff(Qpp,p); Qpppp:=diff(Qppp,p); H:=n*(n-1)*(Q*Qpp-(n-1)/n*Qp^2); if H=0 then ans:=`Hessian is zero: two-dimensional symmetry group` else T:=-n^2*(n-1)*(Q^2*Qppp-3*(n-2)/n*Q*Qp*Qpp+2*(n-1)*(n-2)/n^2 *Qp^3); V:=Q^3*Qpppp-4*(n-3)/n*Q^2*Qp*Qppp+6*(n-2)*(n-3)/n^2*Q*Qp^2 *Qpp-3*(n-1)*(n-2)*(n-3)/n^3*Qp^4; U:=n^3*(n-1)*V-3*(n-2)/(n-1)*H^2; J:=simple(T^2/H^3);K:=simple(U/H^2); j:=subs(p=P,J);k:=subs(p=P,K); Eq1:=simplify(numer(J)*denom(j)-numer(j)*denom(J)); Eq2:=simplify(numer(K)*denom(k)-numer(k)*denom(K)); if Eq1=0 then ans:=`Form has a one-dimensional symmetry group`; else if Eq2=0 then print (` Form has the maximal possible discrete symmetry group`); eqtr:= [solve(Eq1,P)]; tr:=map(radsimp,map(allvalues,eqtr)); else eqtr:=[solve({Eq1,Eq2},P)]; tr:= []; for i from 1 to nops(eqtr) do tr:=map(radsimp,[op(tr),allvalues(rhs(eqtr[i][1]))]); od fi; print(`The number of the projective symmetries`=nops(tr)); ans:=map(l_f,tr); if err=1 then print(`ERROR: Some of the transformations are not linear-fractional`) else if err=2 then print(`WARNING: Some of the transformations are not written in the form polynomial over polynomial`) fi; fi; fi; fi; ans end: |
The program matrices determines the matrix
symmetry corresponding to a given (list of) projective symmetries. As discussed in the text, this only
requires determining an overall scalar multiple, which can be found by substituting the projective
symmetry into the form. The output consists of each projective symmetry, the scalar factor $\mu $,
and the resulting matrix symmetry.
| > | matrices:=proc(form,n,L::list)
local Q,ks,ksi,i,Sf,M; ksi:='ksi'; for i from 1 to nops(L) do Sf:=simplify(denom(L[i])^n*form(L[i])); ks:=quo(Sf,form(p),p); ksi:=simplify(ks^(1/n),radical,symbolic); M[i]:=matrix(2,2,[coeff(numer(L[i]),p)/ksi, coeff(numer(L[i]),p,0)/ksi,coeff(denom(L[i]),p)/ksi, coeff(denom(L[i]),p,0)/ksi]); print(L[i], mu=ksi, map(simplify,M[i])); od; end: |
The auxiliary function l_f uses polynomial division to
reduce rational expressions to linear fractional form (when possible).
| > | l_f:=proc(x)
local A,B,C,S,de,nu,r,R; global err;err:='err'; nu:=numer(x); de:=denom(x); if type(nu,polynom(anything,p)) and type(de,polynom(anything,p)) then if degree(nu,p)+1=degree(de,p) then A:=quo(de,nu,p,'B'); S:=1/A;R:=0 else A:=quo(nu,de,p,'B'); if B=0 then S:=A; R:=0; else C:=quo(de,B,p,'r');R:=simple(r); S:=simplify(A+1/C) fi; fi; if R=0 then collect(S,p) else err:=1;x fi; else err:=2;x fi; end: |
The auxiliary function simple helps to simplify rational
expressions by manipulating the numerator and denominator separately.
The simplified rational expression is returned.
| > | simple:=proc(x)
local nu,de,num,den; nu:=numer(x); de:=denom(x); num:=(simplify((nu,radical,symbolic))); den:=(simplify((de,radical,symbolic))); simplify(num/den); end: |
Example:
| > | f:=p->p^3+1; |
| (1) |
| > | symm(f,3); |
| (2) |
| > | matrices(f,3,%); |
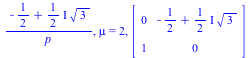 |
|
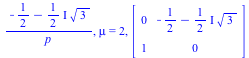 |
|
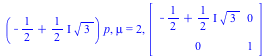 |
|
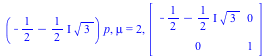 |
(3) |
| > | f:=p->p^2; |
| (4) |
| > | symm(f,3); |
| (5) |
| > | f:=p->p^4+2*I*sqrt(3)*p^2+1; |
| (6) |
| > | symm(f,4); |
| (7) |
| > |
| > |
| > |